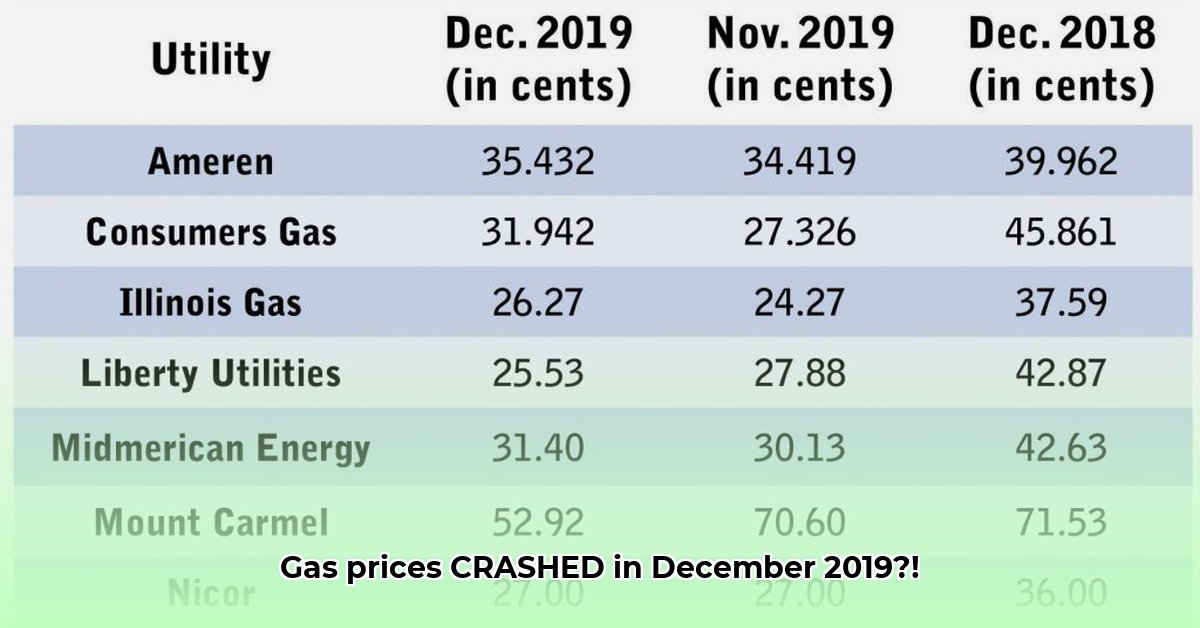
Remember the unexpectedly high gas prices in December 2019? This analysis delves into the factors contributing to that surge, providing insights for drivers, the energy industry, and policymakers. We'll examine historical trends and specific events to understand this significant price fluctuation.
A Retrospective on Gas Prices: 1990-2014
Analyzing gas prices from 1990 to 2014 reveals a general pattern: prices typically rise during the summer driving season and fall during winter months, reflecting seasonal demand fluctuations. However, the data also highlights the influence of fluctuating differences between regular and premium gas prices, indicating the presence of additional market drivers beyond simple seasonal trends. Inconsistencies in the data, however, limit the precision of the overall analysis.
December 2019 Gas Prices: A Detailed Examination
December 2019 presented a notable deviation from typical seasonal patterns. To precisely understand this deviation, we must compare December 2019 prices against previous months of 2019 and against average December prices across several prior years. This comparison allows for the identification of any unusual price spikes that deviate from the historical average.
Unpacking the December 2019 Price Surge: Contributing Factors
The increase in gas prices in December 2019 was likely due to a confluence of factors:
OPEC Actions: The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) significantly impacts global oil supply. Any decisions made by OPEC at the end of 2019 could have affected the world's oil supply, directly influencing gas prices. Were there any policy shifts or production cuts impacting availability?
Geopolitical Events: Unexpected global events can disrupt oil markets and even block oil flow. Did any such occurrences in late 2019 alter the supply chain or create market uncertainty, leading to price increases?
Refinery Issues: Refining oil into gasoline involves multiple stages. Any significant refinery disruptions (maintenance, shutdowns, or unforeseen issues) in the U.S. would likely decrease gasoline supply, thus driving prices upward.
Seasonal Demand: While summer typically sees higher fuel demand, were there unusual seasonal factors in December 2019, such as heightened holiday travel, impacting gasoline consumption and subsequently prices?
Implications and Actionable Insights for Stakeholders
The volatile gas prices of December 2019 offer valuable lessons:
1. Drivers: The importance of fuel-efficient driving habits and price comparison shopping across gas stations cannot be overstated. Monitoring price fluctuations allows for strategic fuel purchasing.
2. Energy Industry: The event underscores the need for energy companies to adapt to shifting market conditions. Strategies could involve enhancing refining efficiency, exploring diverse fuel sources, and investing in alternative energy solutions to reduce oil dependency.
3. Policymakers: The December 2019 experience highlights the need for policies safeguarding energy supplies, reducing reliance on fluctuating global markets, and ensuring infrastructure resilience against unexpected events.
Forecasting Future Gasoline Price Fluctuations: Lessons from December 2019
Predicting future gasoline price fluctuations requires a multifaceted approach involving historical data analysis, identification of key influencing factors (including crude oil prices, refinery operations, geopolitical stability, and seasonal factors), and incorporating predictive modeling techniques. The December 2019 case study serves as a valuable illustration of how multiple variables interact to create price volatility. A robust forecasting model must integrate these diverse influences to deliver reliable predictions within a given confidence interval accounting for uncertainty in external factors.
Key Takeaway: While historical data provides valuable context, accurately predicting future gas prices remains a complex endeavor due to the dynamic interaction of many unpredictable variables. Continuous monitoring of market conditions and ongoing research remain critical for improved forecasting accuracy. Analyzing past events, such as the December 2019 price fluctuation, is crucial for refining predictive models and mitigating future uncertainties.